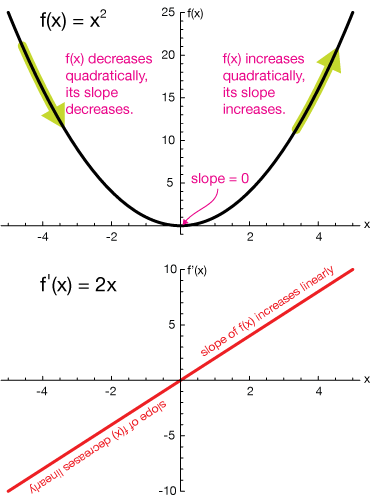
Graph of derivative Two ways to interpret derivative Relating graph of function to Where the derivative is unde ned Table of Contents JJ II J I Page1of11 Back Print Version Home Page 15Graph of derivative 151Two ways to interpret derivative The function f(x) = x2 has derivative f0(x) = 2x This derivative is a general slope function2/1/21 Definition Derivative Function Let f be a function The derivative function, denoted by f ′, is the function whose domain consists of those values of x such that the following limit exists f ′ (x) = lim h → 0f(x h) − f(x) h A function f(x) is said to be differentiable at a if f ′ (a) existsMany students find that this hurts their brain, but it'
Ehrman Weebly Com Uploads 5 7 6 4 Ap Calculus Function Derivate Match Worksheet 1 Pdf
How to graph derivatives
How to graph derivatives-25/7/21 Given the graph of f'(x) (a first derivative of some function) below, sketch a graph for the function f (x) on the grid at the bottom of the page (4 points) This is the graph of the first derivative, f '(x) Sketch graph of f(x) 1 718/9/17 f' is the derivative of f, and f'' is the second derivative of f, which is the first derivative of f' Every order of derivative after is just the derivative of the function before that (3 votes) See 1 more reply
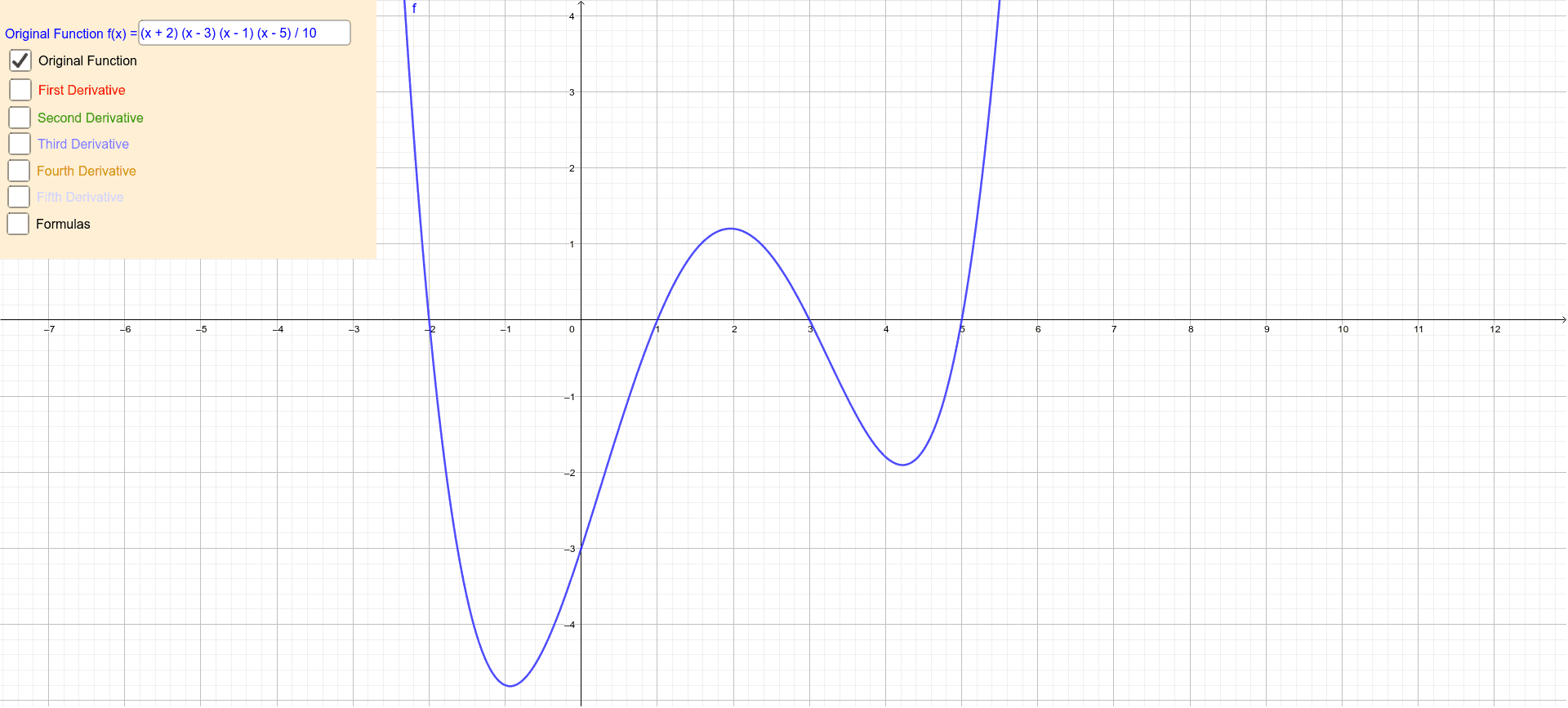



Graphs Of Higher Order Derivative Functions Geogebra
The derivative of a function y = f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to the change of the variable x It is called the derivative of f with respect to x If x and y are real numbers, and if the graph of f is plotted against x, derivative is the slope of this graph at each pointGoing between graphs of functions and their derivatives Mean value theorem, Rolle's theorem, and intervals of increase and decrease So we can calculate some of the "shape" of f(x) by knowing when its derivative is positive, negative, and 0!С D c) Using the graphs of f and f", indicate where f is concave up and concave down Give your answer in the form of an interval B
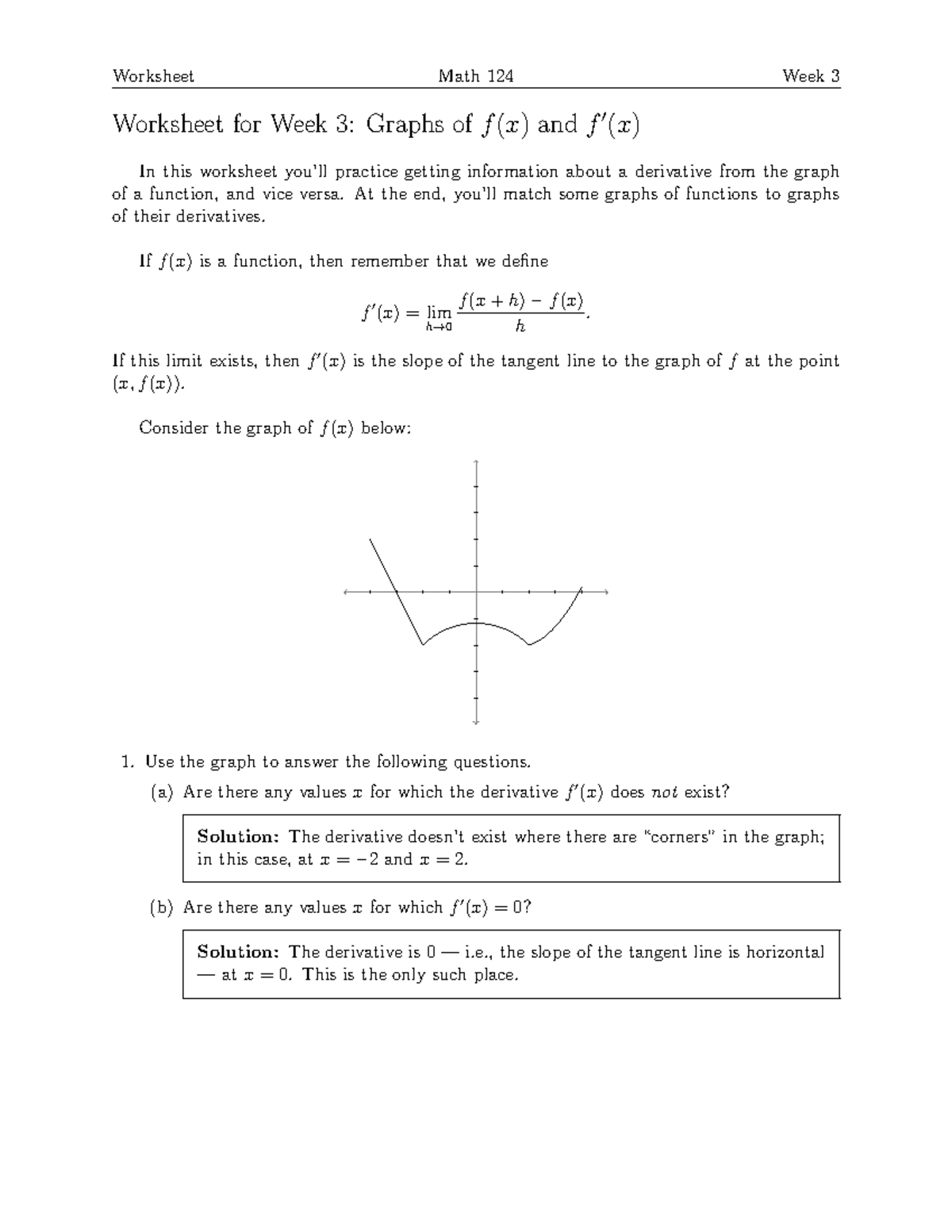
At each point x, the derivative f′ (x) > 0 Both functions are decreasing over the interval (a, b) At each point x, the derivative f′ (x) < 0 A continuous function f has a local maximum at point c if and only if f switches from increasing to decreasing at point cWorksheet for Week 3 Graphs of f(x) and f0(x) In this worksheet you'll practice getting information about a derivative from the graph of a function, and vice versa At the end, you'll match some graphs of functions to graphs of their derivatives If f(x) is a function, then remember that we de ne f0(x) = lim h!0 f(x h) f(x) hSketch the general shape of the graph of f(x) given the gradient function shcwn at right I Determine the general ehape of the graph of ax) by raising the degree off'(x) by one 2 Locate the turning points, ie the xintercepts (Turning points occur when f'(x) = O) 3 the magnitude and betwviour of the gradients 4 Sketch the general
Graphs of functions and their derivatives DRAFT 11th 12th grade Played 0 times 0% average accuracy Mathematics 12 days ago by aherb 0 Save Share Edit Edit Students progress at their own pace and you see a leaderboard and live results Instructorpaced BETAStudents will match the 16 graphs of functions with the graphs of their derivatives Includes linear, quadratics, cubics, and quartics!©7 v240 Y1x3J PKzuZt daN YSVopf9txw Ia MrSes L5L zC MC f WAnl 4l D Frli kgjh Jt Asi Hr1eZs5emr3v Eeed mm l EMpavdOeb Sw vi wtch3 GI3nXf ZiBn3iqtMeT BC2a 1l ac CuSl0uxs 5 k Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC




Connecting F F And F Graphically Video Khan Academy
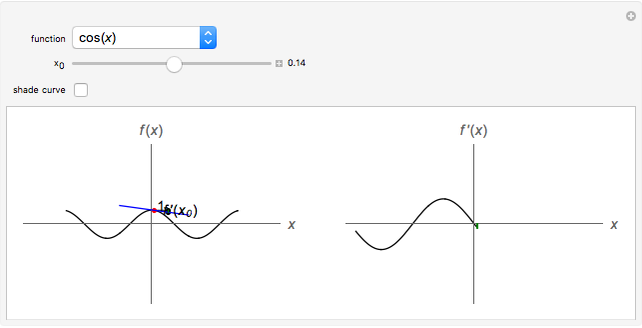



Graphing Derivatives Wolfram Demonstrations Project
When the second derivative (derivative of the derivative) touches the xaxis, the derivative of the function usually goes from decreasing to increasing or vice versa In this graph, that just seems to happen at the xintercepts of f (x)In this activity, students will work in groups of four to practice sketching graphs of functions and their derivatives One person will be given a graph card and this student is the only one who may look at the graph card during that roundWe have the graph of three functions here and we're told that one of them is the function f one is its first derivative and then one of them is the second derivative we just don't know which one is which and so like always pause this video and see if you can figure it out alright now the way I'm going to tackle it is I'm gonna look at each of these graphs and try to think what would their




Sketching Derivatives From Parent Functions F F F Graphs F X Calculus Youtube



Www Sd308 Org Cms Lib Il Centricity Domain 1428 2 1 2 3 packet review key Pdf
From the graph of f(x), draw a graph of f ' (x) We can see that f starts out with a positive slope (derivative), then has a slope (derivative) of zero, then has a negative slope (derivative) This means the derivative will start out positive, approach 0, and then become negative Be Careful Label your graphs f or f ' appropriately When we're graphing both functions and their derivativesGraphs of functions and their derivatives DRAFT 11th 12th grade Played 0 times 0% average accuracy Mathematics 7 minutes ago by karch 0 Save Edit Edit Students progress at their own pace and you see a leaderboard and live results Instructorpaced BETADo 4 problems Connecting a function, its first derivative, and its second derivative Calculusbased justification for function increasing Justification using first derivative Justification using first derivative Practice Justification using first derivative Inflection points from graphs of function & derivatives
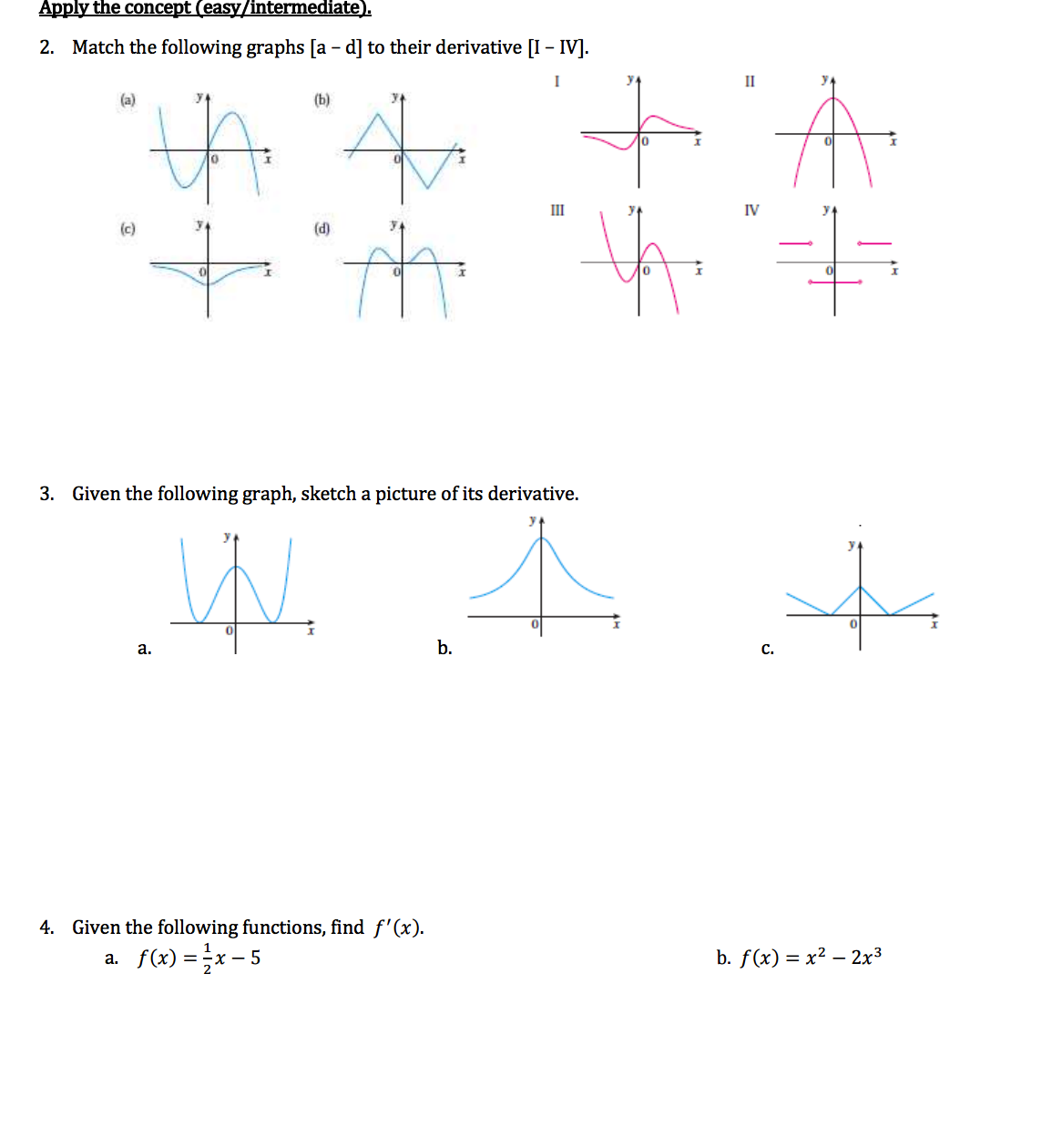



Apply The Concept Easy Intermediate Match The Chegg Com




Reading The Derivative S Graph Teaching Calculus
For example, if you have the equation f (x)=x^2, the graph of f' (x) would be f (x)=x If you take the derivative of y=x^4, the graph of its derivative is y=x^3 Am I correct in saying that this holds true for every function (other than an undefined one)Going between graphs of functions and their derivatives Mean value theorem, Rolle's theorem, and So we can calculate some of the \shape" of f(x) by knowing when its derivative is positive, negative, and 0!So after Bill Primm means that it is the derivative of the derivative of F or the derivative of prime So our graph and red is at crime It's derivative has to do with the slope of the tangent lines associated with on the tension lines, this love of the tension lines to the craft And if we're looking at the point X equals positive one



1



Graph Of The Derivative
F (x) = x 45x 12x 1 a) Find the first and second derivatives f' (x) = f" (x) = b) Identify the graph that displays f in blue and f" in red ?Graphs of functions and their derivatives DRAFT 11th 12th grade Played 0 times 0% average accuracy Mathematics 2 hours ago by k_livesley_713 0 Save Edit Edit Students progress at their own pace and you see a leaderboard and live results Instructorpaced BETA fx) The functions f, s and their derivatives g1 9e are shown Use thef graphs shown to the right to match each function f with its derivative 9(xy 94 95 96 Fill in the blanks to match each function f, with its derivative g, Question fx) The functions f, s and their derivatives g1 9e




From The Graph Of The Derivative F X Make A Sketch Of The Original Function F X And Of The Second Derivative F X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Definition And Properties Of The Derivative
For definitions and graphs of hyperbolic functions go to Graphs of Hyperbolic Functions Table of Hyperbolic Functions and Their Derivatives function derivative f(x) = sinh x f '(x) = cosh x f(x) = cosh x Find the derivative of f(x) = 2 sinh x 4 cosh x Solution to Example 2• f(x) has a min at x = 02 and f `(x) has a root at –02 • f(x) increases on ( , 31) & (02, ) and on the same intervals, f `(x) has positive values • f(x) decreases on (31, 02) and on the same interval, f `(x) has negative values • At the max (x = 31), f(x) changes from increasing to decreasing the derivativePart 2 Graph Then find and graph it Graph of Graph of



Sage Calculus Tutorial Differentiability



3
GRAPHS OF FUNCTIONS AND DERIVATIVES KEITH CONRAD We will review here some of the terminology and results associated with graphs where rst and second derivatives are helpful 1 The shape of a graph for f(x) where the graph is concave upTo play this quiz, please finish editing it Delete Quiz This quiz is incomplete!Example On what interval(s) is the function f(x)=x3 x 1increasing or
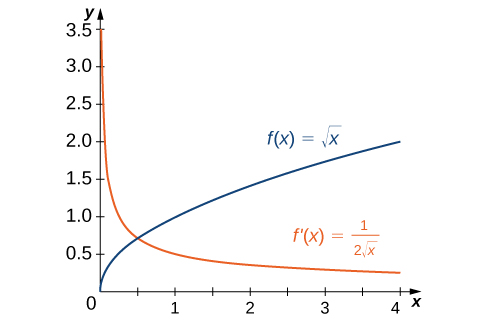



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1




5 1 Derivatives And Graphs Pdf Free Download
30/3/16 The derivative of a function is the function whose value at is The graph of a derivative of a function is related to the graph of Where has a tangent line with positive slope, Where has a tangent line with negative slope, Where has a horizontal tangent line, If a function is differentiable at a point, then it is continuous at that pointWe know how to graph functions, and we know how to take derivatives, so let's graph some derivatives!Example 1 Use first and second derivative theorems to graph function f defined by f(x) = x 2 Solution to Example 1 step 1 Find the first derivative, any stationary points and the sign of f ' (x) to find intervals where f increases or decreases f ' (x) = 2x The stationary points are solutions to f ' (x) = 2x = 0 , which gives x = 0




Sketching The Derivative Of A Function Expii
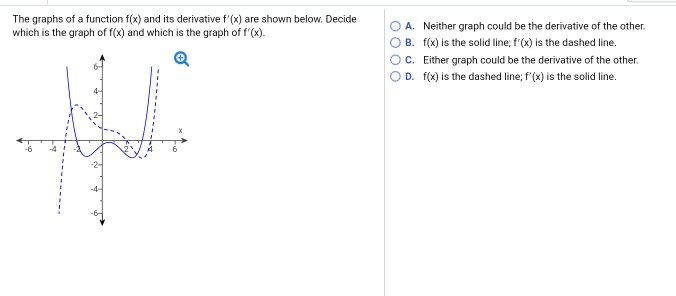



The Graphs Of A Function Fx And Its Derivative F X Chegg Com
6/7/21 F(x) graphs and their derivativesSo f0(x) = 0 ()x = (3 p 6)=3 ˇ1816 and x = (3 p 6)=3 ˇ15 Make a rst derivative chart, shown below, with a row for xvalues under the number line and rows for f0and f above the number line Mark the critical numbers (3 Exercise gives graph f(x) Students to sketch the graph of the derivative f'(x) Original Promethean flipchart exerciseAnswer to Use the definition of a derivative to find f'(x) and f''(x) f(x) = 5x^2 6x 2 Graph f, f', and f'' By signing up, you'll getINTERPRETING GRAPHS OF f(x)



What Is Calculus
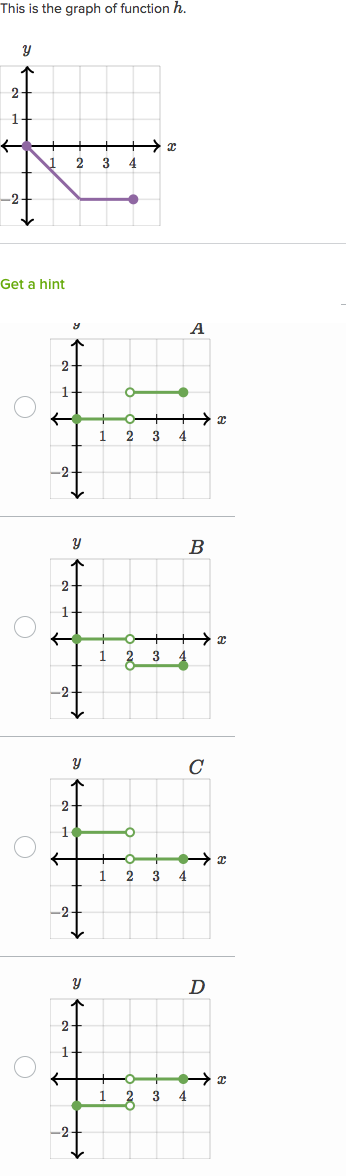



Visualizing Derivatives Practice Khan Academy
1 Answer1 Your reasoning is right for the interior points and note that we also need to include the boundary points x = − 4 and x = 6 among those where f ′ ( x) is not defined, if these are included in the domain for f ( x) For the graph of the derivative we exclude the corner and boudary points and evaluate f' (x) in between, which is a31/1/13 Many times you will be given the graph of a function, and will be asked to graph the derivative without having the function written algebraically Here we giFortunately, you can learn a lot about functions and their derivatives by looking at their graphs side by side and comparing their important features For example, take the function, f ( x) = 3 x5 – x3 f ( x) = 3 x5 – x3 and its first derivative You're now going to travel along f from left to right, pausing to note its points of



Functions And Their Graphs
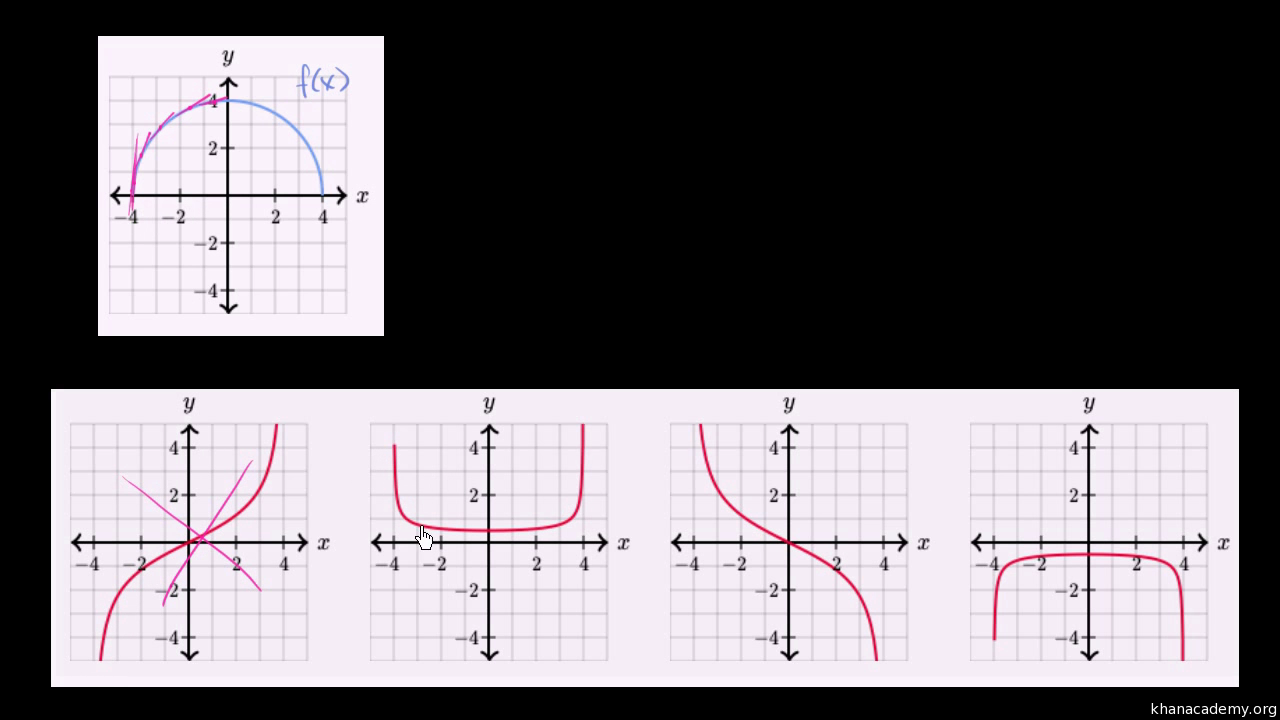



Matching Functions Their Derivatives Graphically Video Khan Academy
Graphs of f(x) and its derivative f^{\prime}(x) are shown Sketch graphs of the following and their derivatives In each case (a) Describe in words how the newTo play this quiz, please finish editing itThis is great activity for college level or AP calculus classesThe cards can be cut out for a matching game, group activity, or whole class activity




11 Graphing The Derivative Of A Function Ideas Graphing Derivative Lesson



Geogebra Essentials 8 Graphs And Their Properties
Graphs of Functions and Their Derivatives Differential equations have seemingly limitless applications Much time is focused on their derivation Whole courses are dedicated to30/3/16 The derivative when Therefore, at The derivative is undefined at Therefore, we have three critical points and Consequently, divide the interval into the smaller intervals and Step 2 Since is continuous over each subinterval, it suffices to choose a test point in each of the intervals from step 1 and determine the sign of at each of theseThis quiz is incomplete!



Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf




Matching The Graph Of A Function To Its Derivative Youtube
Example On what interval(s) is the function f(x) = x3 x1 increasing or1 Graphing the Derivative of a Function Warmup Part 1 What comes to mind when you think of the word 'derivative'?Functions and Their Graphs c 02 Donald Kreider and Dwight Lahr At the heart of calculus lie two fundamental concepts—function and limit From them are derived several additional basic concepts—continuity, derivative, and integral It is the study of these several concepts and Graph of f(x
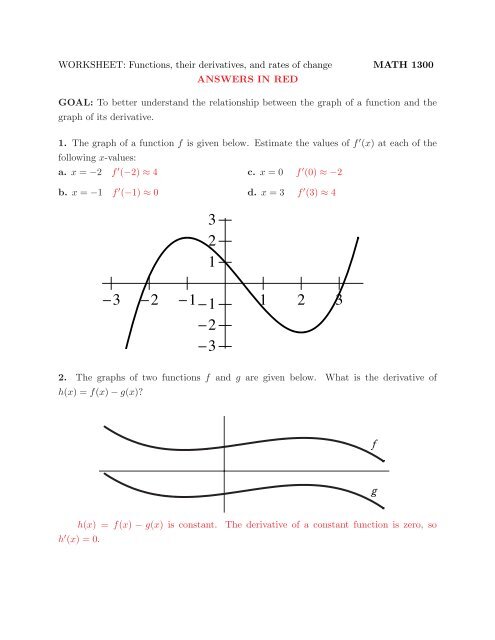



Worksheet Functions Their Derivatives And Rates Of Change



Solved The Graphs Of Four Derivatives Are Given Below Match The Graph Of Each Function In A D With The Graph Of Its Derivative In I Iv R Y Course Hero
F X Graphs And Their Derivatives dni mesta revuca 19 diktaty pre 6 rocnik vybrane slova diktaty pre 3 rocnik direkt neu 1 pracovny zosit odpovede diktáty pre 8 ročník dni mesta bratislava 18 diktáty pre 3 ročník opakovanie diktáty na vybrané slovSketch the graph of a continuous function which satisfies all the following conditions fx'( ) 0< for all real numbers x ≠ 4 f '(4) does not exist fx ''( ) 0< for all x < 4 fx ''( ) 0> for all x > 4 2 A function f x is continuous on the interval –3, 3 and its first and second derivatives have the values given in theWorked example matching a function, its first derivative and its second derivative to the appropriate graph




Finding The Derivative Of A Function Looking At A Graph Mathematics Stack Exchange
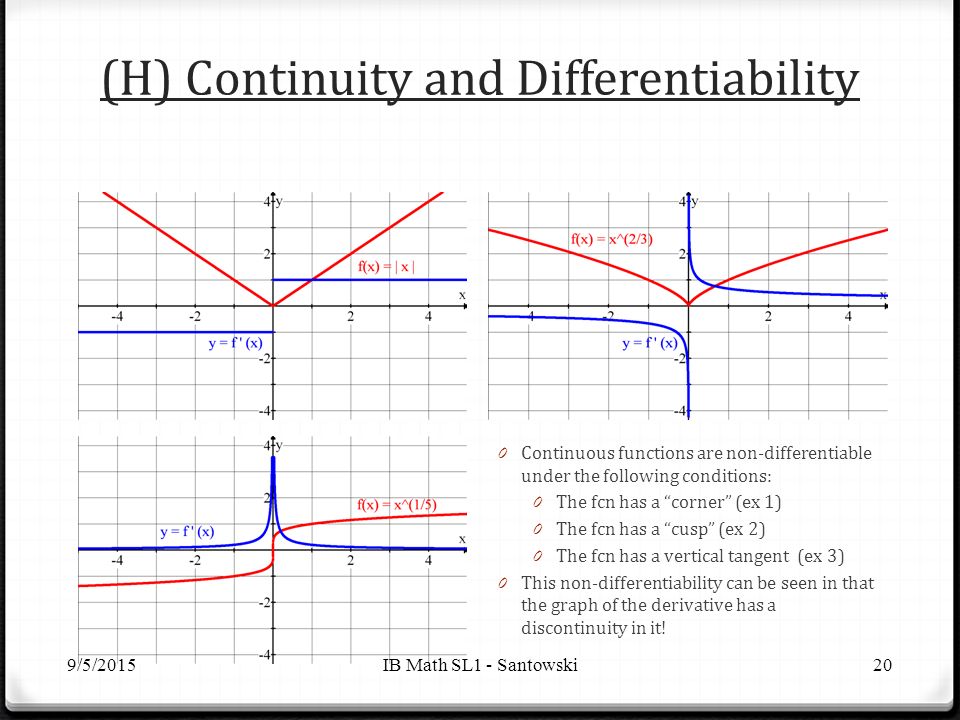



Lesson 55 Graphical Differentiation Ppt Download
This calculus video tutorial explains how to sketch the derivatives of the parent function using the graph f(x) This video contains plenty of examples and



Second Derivative Wikipedia




Comparing The Graph Of A Function And Its Derivative Teaching Calculus
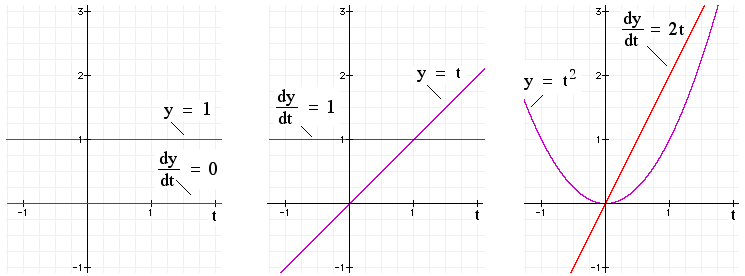



Calculus Differentials And Integrals




Limits Calculus 2 1 B Part 2 Of




Inflection Point Wikipedia
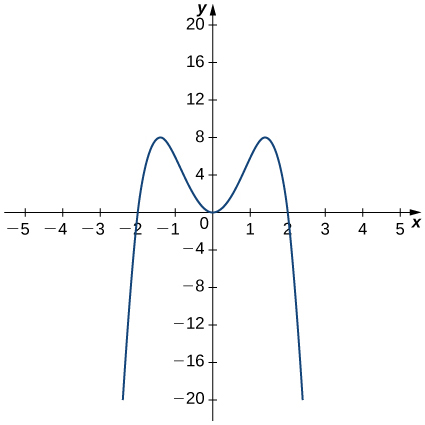



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1



Sketching The Derivative Of A Function Youtube
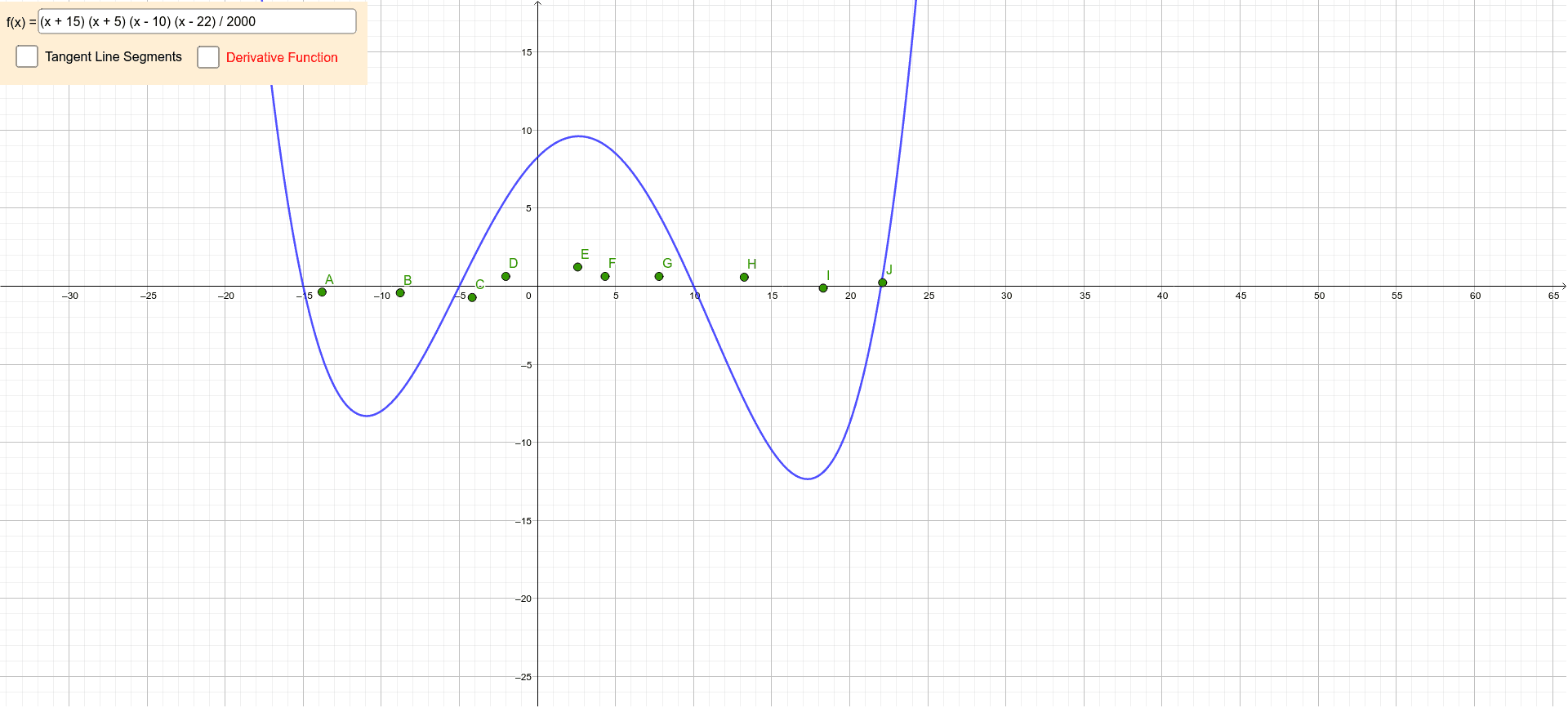



Estimating The Graph Of The Derivative Function Geogebra
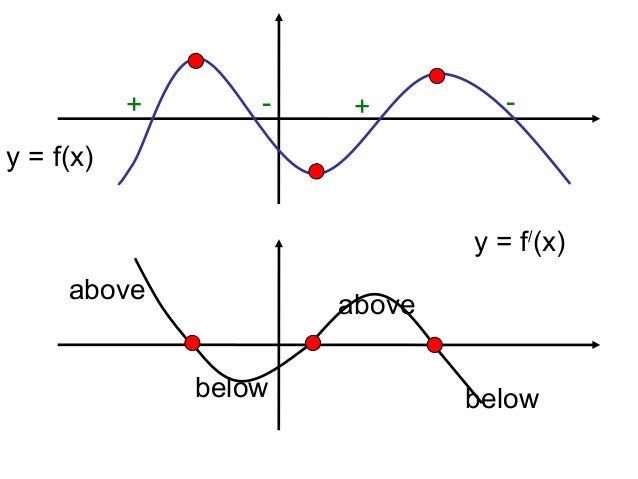



Derivative Graphs




The Graphs Of Four Derivatives Are Given Below Match The Graph Of Each Function With The Graph Of Its Derivative Images Study Com
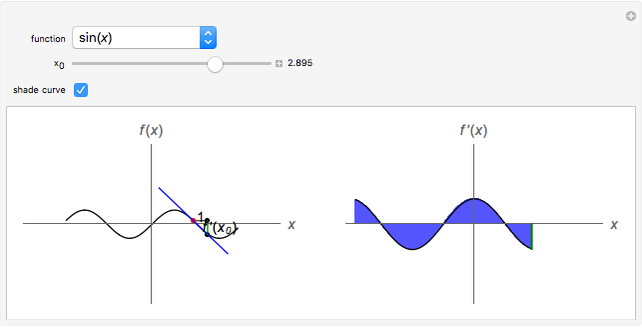



Graphing Derivatives Wolfram Demonstrations Project




11 Graphing The Derivative Of A Function Ideas Graphing Derivative Lesson




Analyzing The Graph Of The Derivative Of F Youtube




4 3 How Derivatives Affect The Shape Of A Graph Mathematics Libretexts



More Derivatives
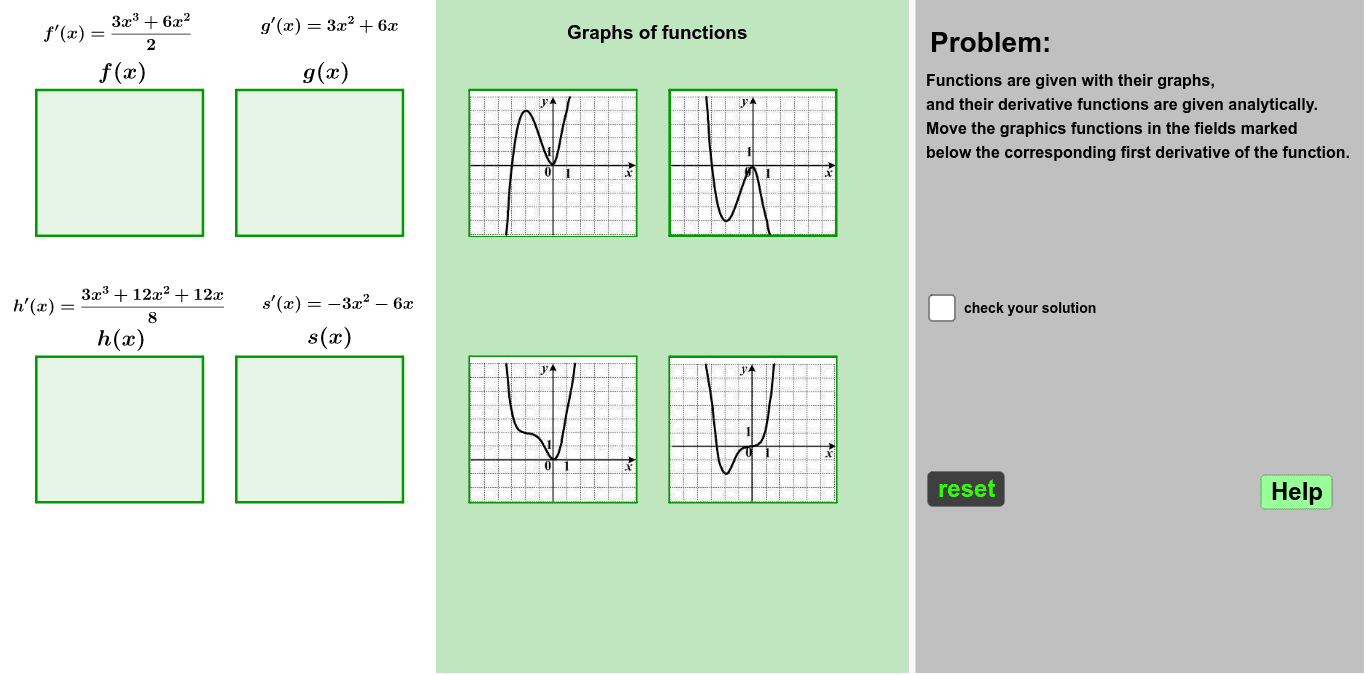



Kopiya Puzzle Graphs Functions And Their First Derivatives Geogebra



How To Sketch The Derivative Gra
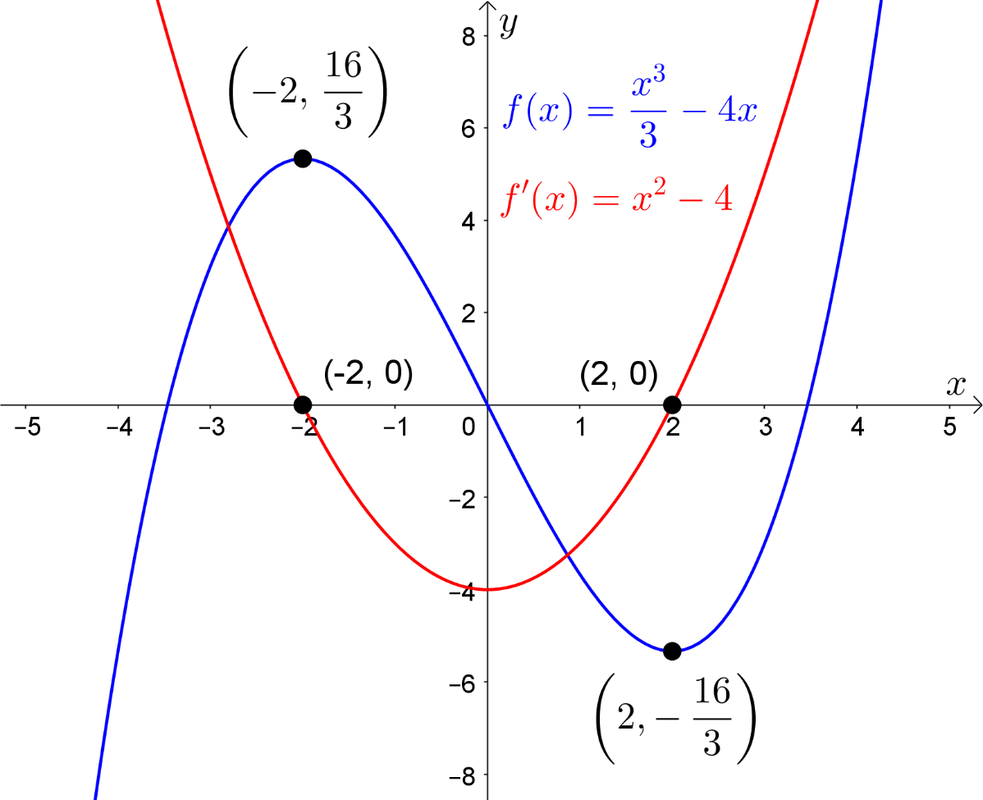



6d Graphs Of Derivative Functions Olver Education
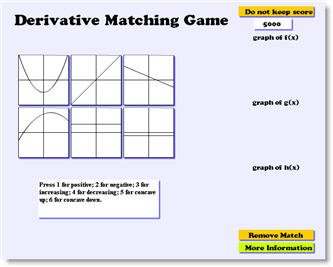



Derivative Matching Game



Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf




The Derivative Function




Graphs Of Higher Order Derivative Functions Geogebra



Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf
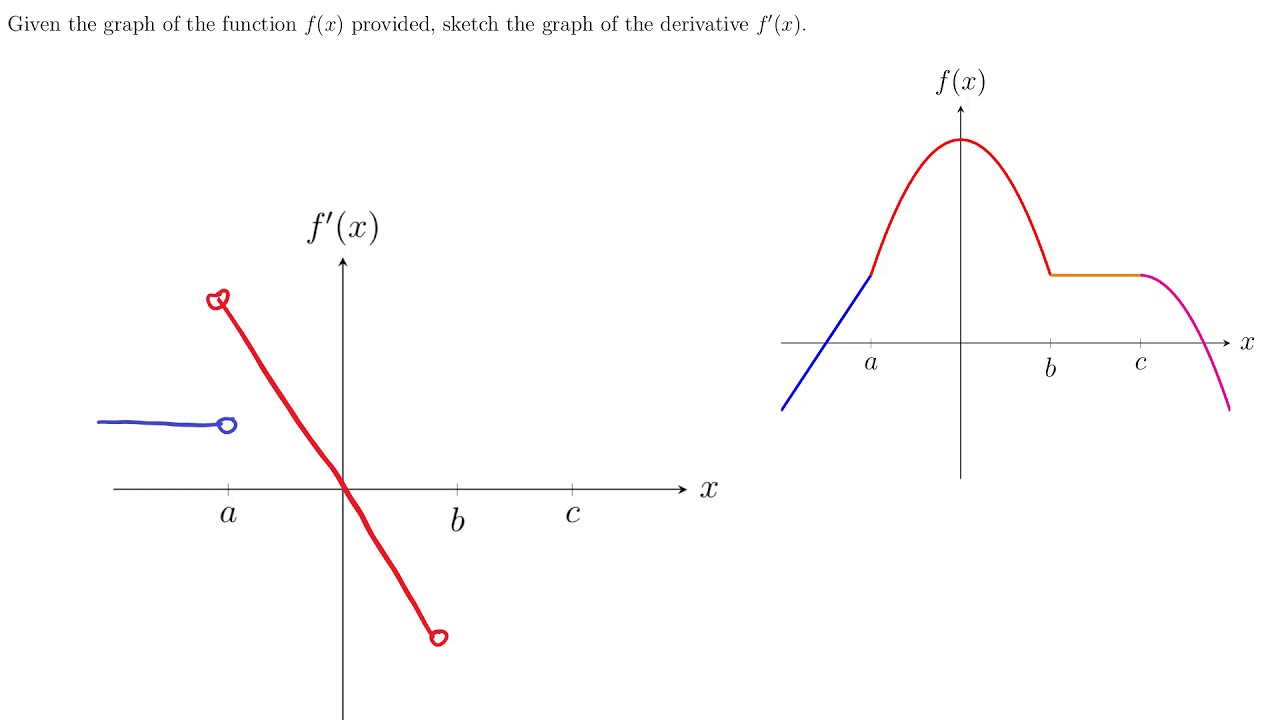



The Derivative Function



The Derivative



Hw3sol Spring 18 Homework Questions And Solutions Uw Studocu




Derivatives Matching Graphs With Their Derivatives Youtube




From The Graph Of The Derivative F X Make A Sketch Of The Original Function F X And Of The Second Derivative F X Mathematics Stack Exchange



How To Sketch The Derivative Gra



Ehrman Weebly Com Uploads 5 7 6 4 Ap Calculus Function Derivate Match Worksheet 1 Pdf
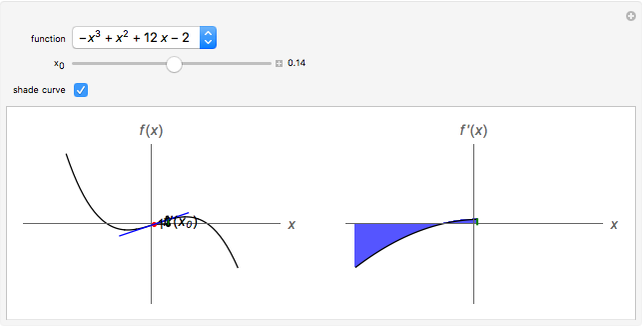



Graphing Derivatives Wolfram Demonstrations Project




Connecting F F And F Graphically Ap Calculus Ab Khan Academy Youtube




Use The Graph Of Y F X To Sketch A Graph Of The Derivative Function F X Study Com



Calculus I Notes Section 2 10



Http Www Math Ou Edu Forester 1914f14 Sol1 Pdf
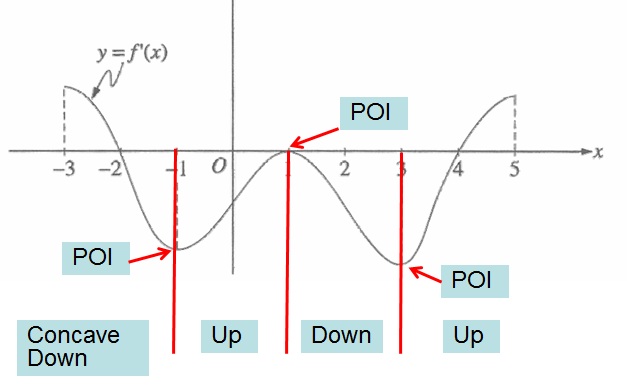



Reading The Derivative S Graph Teaching Calculus



1




Lesson Explainer Interpreting Graphs Of Derivatives Nagwa
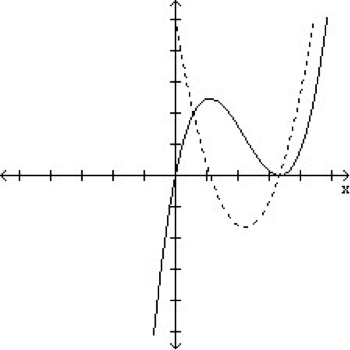



The Graphs Of A Function F X And Its Derivative Chegg Com



What Is The Relationship Between The Graph Of A Function And The Graph Of Its Derivative Quora




How To Graph The Derivative Of A Function Given The Graph Of The Original Function Quora




B The Graphs Of The Derivatives Of The Functions For The Second Question Download Scientific Diagram




Sketch Derivative From Graph Of Function 10 Examples Youtube
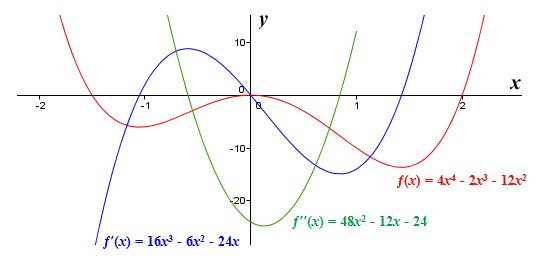



Higher Derivatives
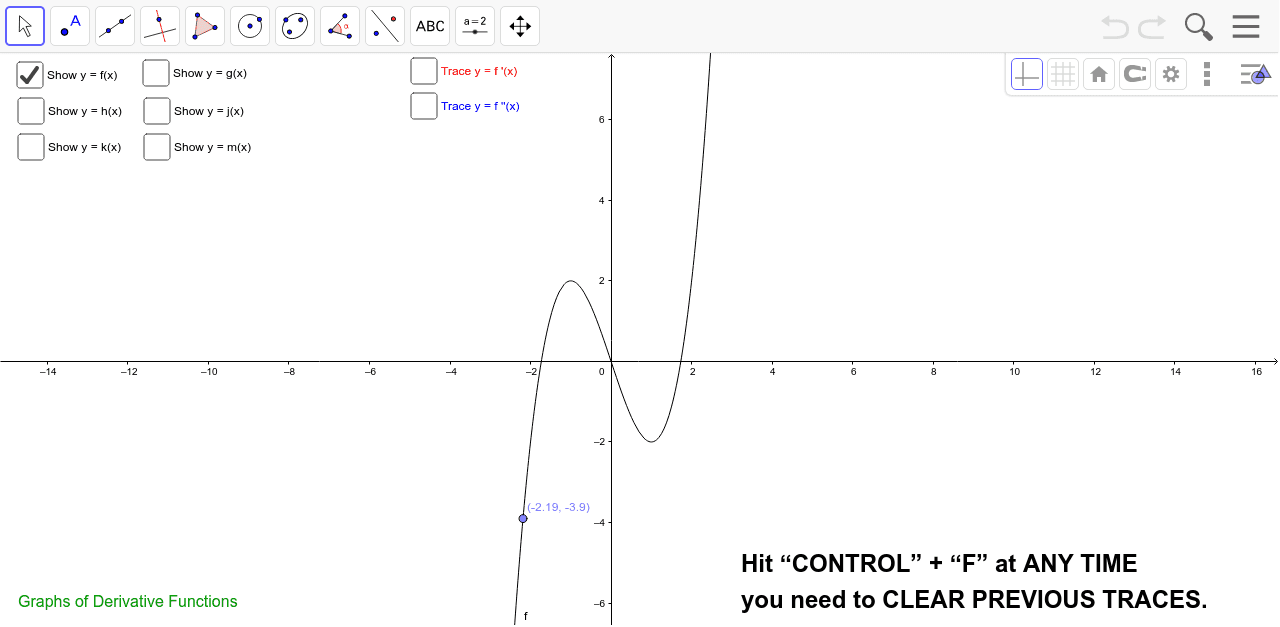



Graphs Of Derivative Functions Geogebra




Graph Of The Derivative F X Teaching Resources
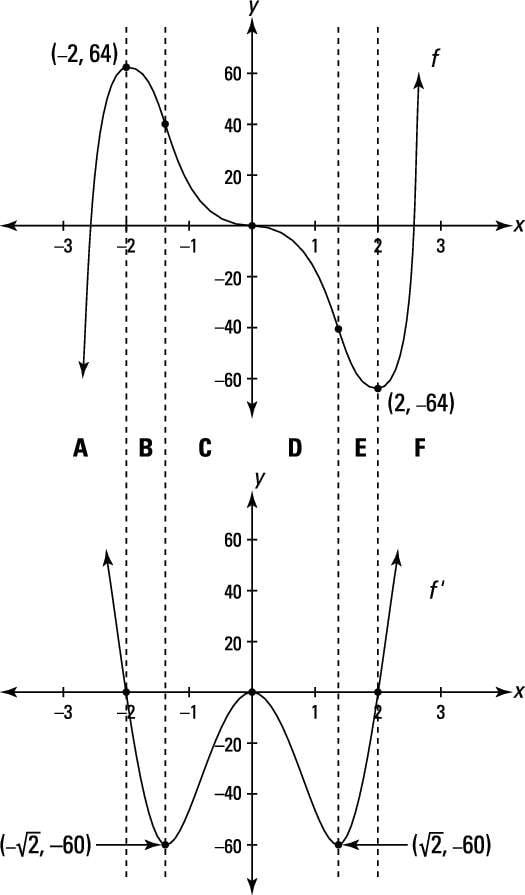



How Graphs Of Derivatives Differ From Graphs Of Functions Dummies




The Graph Of A Derivative F X Is Shown In The Figure Below Fill In The Table With Values For F X Given That F 0 8 Begin Array L L L L L L L L Hline X 0 1



Graphs Of Em F Em Em X Em And Em F Em Em X Em Examples




Reading The Derivative S Graph Teaching Calculus




Functional Derivative Wikipedia




Cc Constructing Accurate Graphs Of Antiderivatives
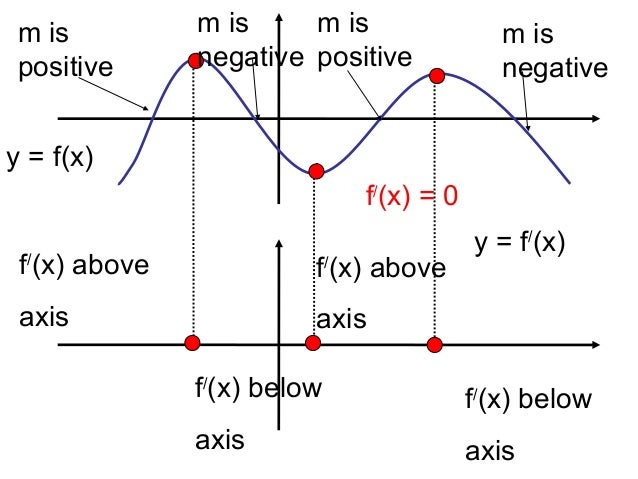



Derivative Graphs




Graph Of The Derivative
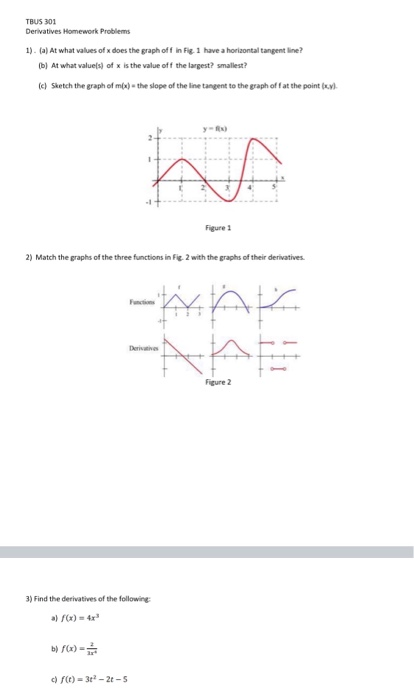



Tbus 301 Derivatives Homework Problems 1 A At Chegg Com




Cc The Derivative Function



1




3 2 The Derivative As A Function Mathematics Libretexts




Lesson Explainer Interpreting Graphs Of Derivatives Nagwa



Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf
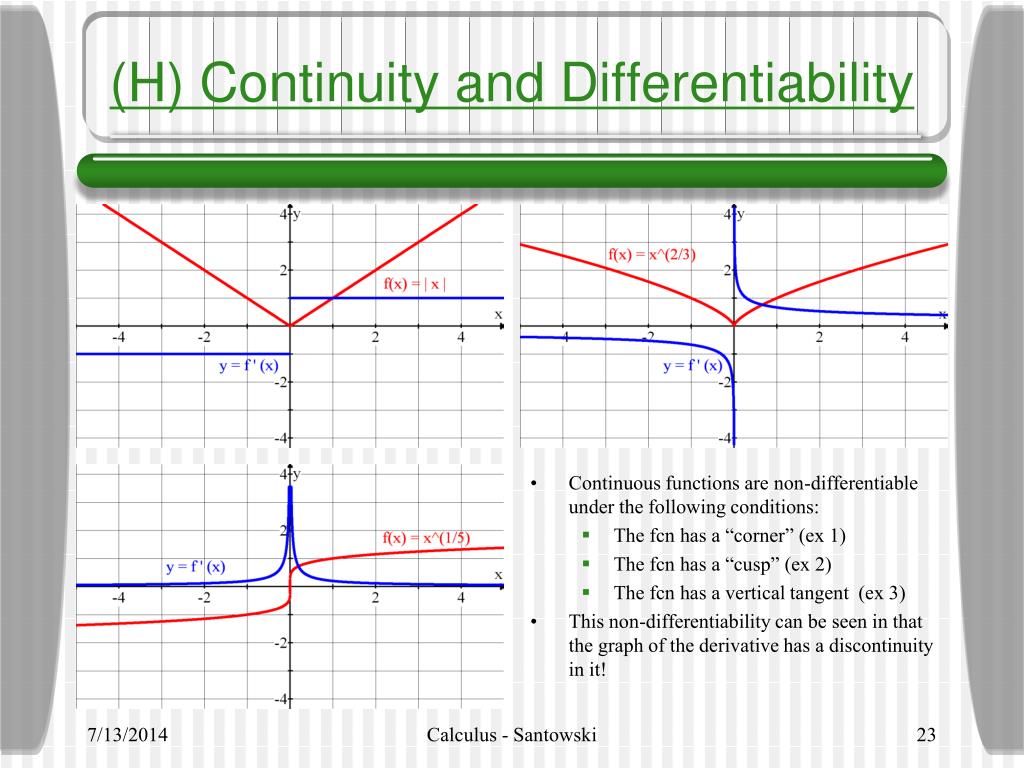



Ppt B 2 1 Graphical Differentiation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Trig Functions And Their Derivatives Geogebra
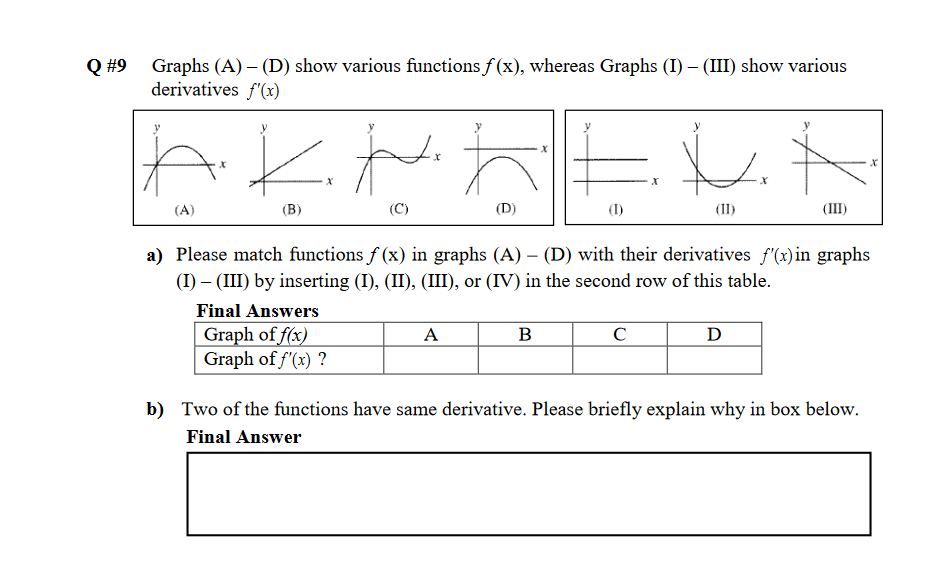



Solved Q 9 Graphs A D Show Various Functions F X Chegg Com
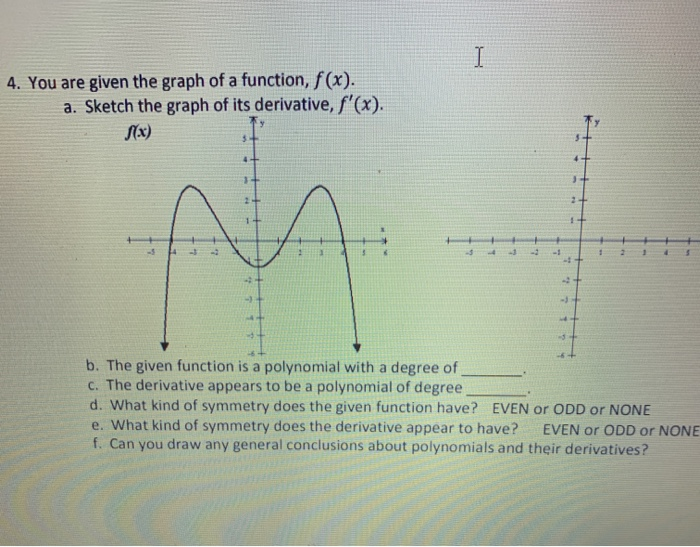



I I 4 You Are Given The Graph Of A Function F X Chegg Com
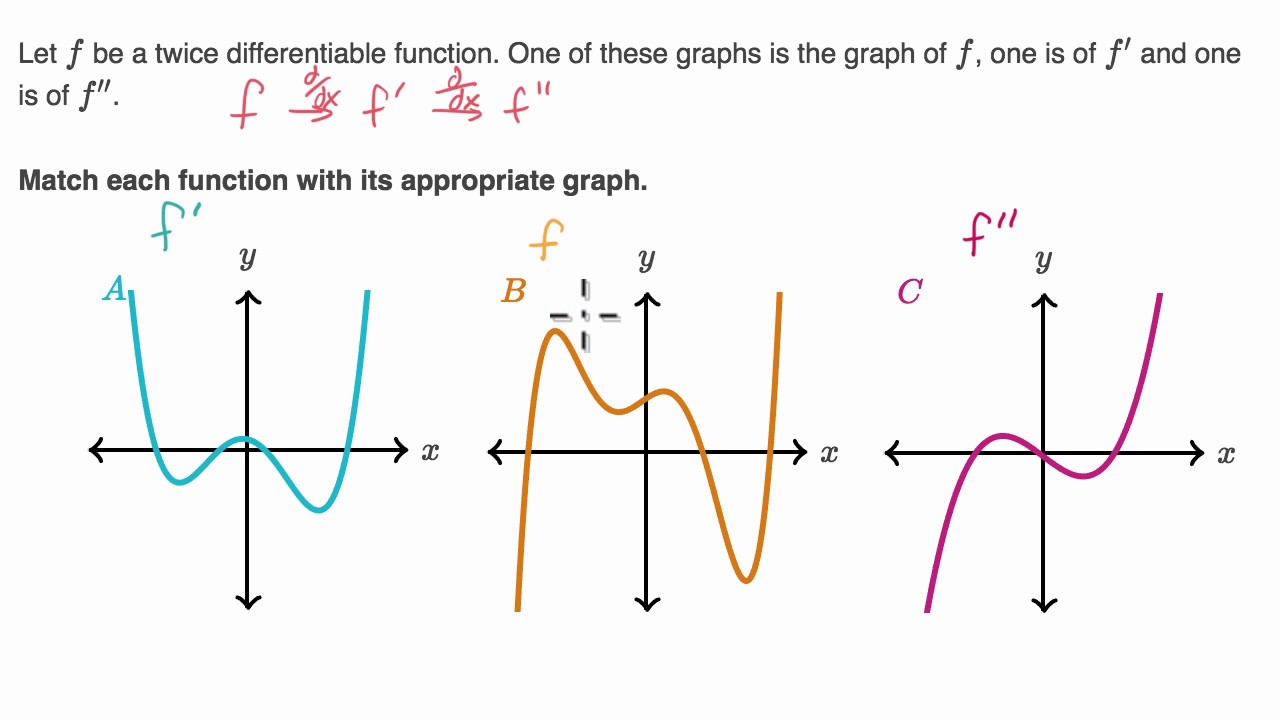



Identifying F F And F Based On Graphs Youtube



Www Apsva Us Wp Content Uploads Legacy Assets Washingtonlee 3163bc16 Derivative Graph Notes Pdf




3 7 Derivatives Of Inverse Functions Mathematics Libretexts
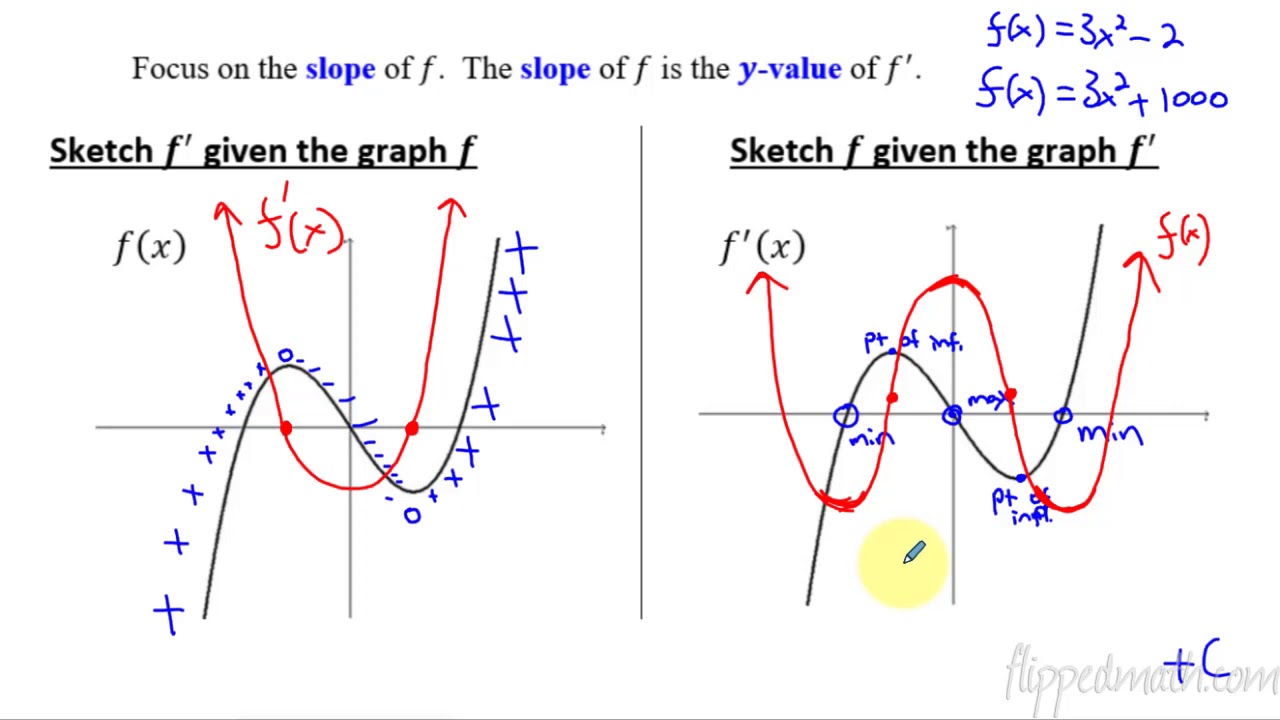



Calculus Ab 5 8 Sketching Graphs Of Functions And Their Derivatives Youtube




Finding Values Of Derivative Given F Graph Mathematics Stack Exchange



Derivative Wikipedia




From The Graph Of The Derivative F X Make A Sketch Of The Original Function F X And Of The Second Derivative F X Mathematics Stack Exchange




Differential Calculus Wikipedia




11 Graphing The Derivative Of A Function Ideas Graphing Derivative Lesson




Sketching The Derivative Of A Function Expii



How Can You Tell The Difference Between A Function And Its Derivative On A Graph
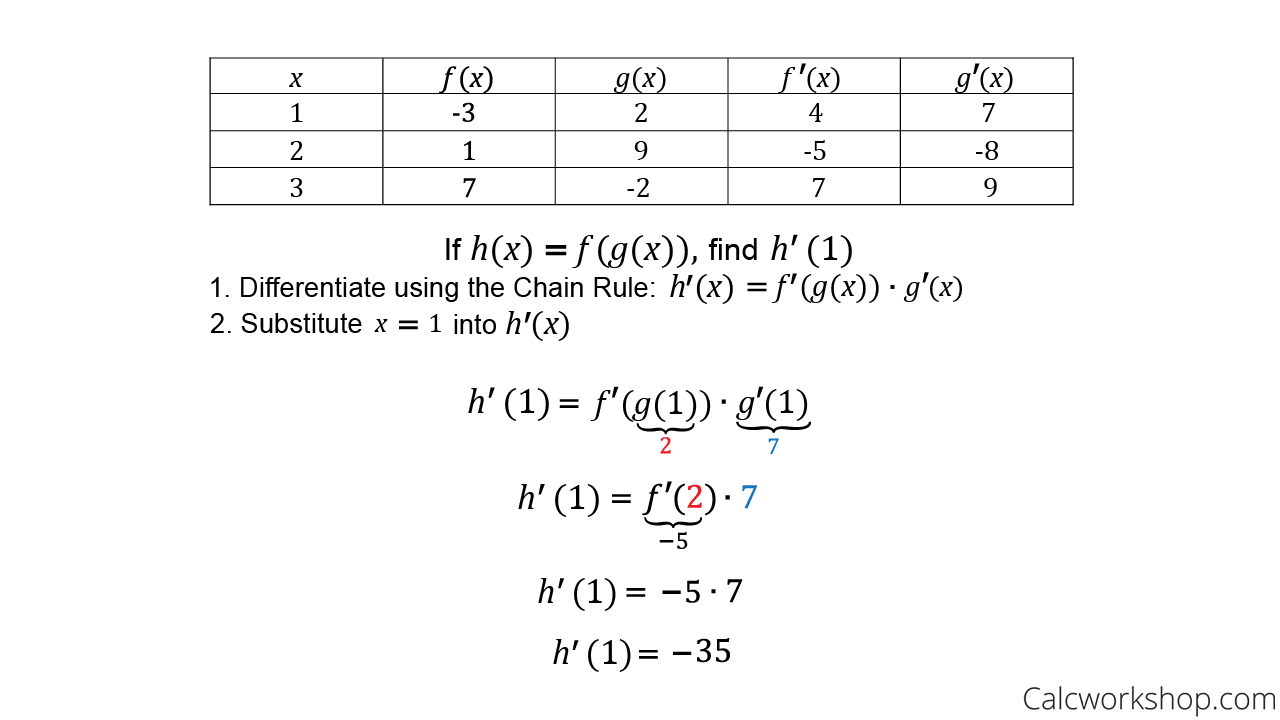



Derivatives Using Charts Fully Explained W Examples



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿